Adults aged 65 years or older have high chances of having Arthritis, yet can affect people of all ages including children.
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints. There are many types of the disease, both inflammatory and non-inflammatory that effect joints and other connective tissues in the body.
Arthrosis is limitation of a joint without inflammation.
Arthritis is common among adults aged 65 years or older, but it can affect people of all ages including children. In 2017, 50.4 percent of those aged 65 years and older had doctor-diagnosed it in some form in the United States. In 2017, around 25 percent of women had doctor-diagnosed it in some form in United States.
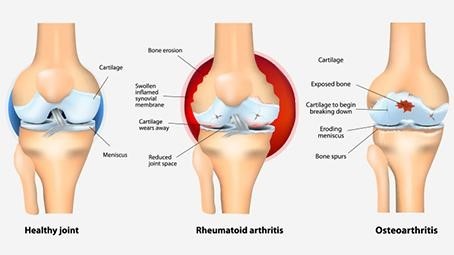
There are many types of arthritis that effect joints but the most common types of the disease are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis (OA):
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of Arthritis that affects the cartilage, ligament, joint lining, and underlying bone of a joint. The breakdown of these tissues eventually leads to pain and joint stiffness. The joint most often affected by Osteoarthritis are those that have heavy use such as hip, knee, hand, spine, base of thumb and the joint of big toe.
Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA):
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the tissues of the body specifically connective tissues leading to joint inflammation, pain and degeneration of the joint tissues. It can occur at any age and it associates with fatigue and prolong stiffness after rest.
People with Rheumatoid Arthritis often have an elevated Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR, also known as sed rate) or C-Reactive Protein (CRP) level, which may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
In 2019, percentage of adults with the disease by state was around 41 percent of all adults in West Virginia, compared to 21 percent of those in Texas.
There is no single cause of all types of this disease. Possible cause may include injury, abnormal metabolism, inheritance, infection and immune system dysfunction.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Symptoms may develop gradually and suddenly. Early sign and symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness and joint immobility. Clinical Signs and Symptoms are pain, impaired mobility, impaired muscle performance, impaired balance, activity limitations and participation restriction, redness, tenderness and swelling.
There are many risk factors that cannot modify, include:
- Age: the risk of developing most types of arthritis increases with age.
- Sex: most types of arthritis are more common in females, and 60 percent of all people with the disease are female. Gout is more common in males than females.
- Genetic factors: specific genes associate with a higher risk, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and ankylosing spondylitis.
Risk Factors of Arthritis
Risk factors that can modify through treatment are:
- Overweight and obesity: excess weight can contribute to both the onset and progression of knee osteoarthritis.
- Joint injuries: damage to a joint can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis in that joint.
- Infection: many microbial agents can infect joints and trigger the development of various forms of arthritis.
- Occupation: certain occupations that involve repetitive knee bending and squatting relate to osteoarthritis of the knee.
Treatment:
- Physical Therapy
- Diet
- Medication
- Surgery
Self-management of disease demands physical activity and achieving and maintaining healthy life style. One should get regular checkup and protect joints from unnecessary stress.
Physical Therapy:
The doctor will likely recommend a course of physical therapy to help manage some of the symptoms. Treatment for arthritis aims to relieve pain, minimize joint damage, muscle guarding and relaxation technique, improve of maintain function and quality of life.
Warm water therapy is considered as powerful tool for management of arthritis. Exercises in warm water supports weight and puts less pressure on the muscles and joints.
Also See: Color Psychology: How colors define our Mood and Human Behavior
Avoid smoking and not drinking excess alcohol can help people with arthritis maintain their overall health.
Diet:
There is no specific diet that treats arthritis but some may reduce inflammation. Mediterranean diet can provide some of the nutrients that are good for joint health such as fish, nuts seeds, fruits and vegetables. One should avoid Night shade vegetables (e.g. tomatoes contains a chemical such as Solanine that trigger arthritis pain). Research findings are mixed when it comes to these vegetables but some people have reported a reduction in arthritis symptoms after avoiding night shade vegetables.
Medications:
Drugs play an important role in treating arthritis such as
Analgesics, such as hydrocodone (Vicodin) or Acetaminophen (Tylenol), are effective for pain management, but don’t help decrease inflammation.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), such as Ibuprofen (Advil) and salicylates, help control pain and inflammation. Salicylates can thin the blood, so they should be used very cautiously with additional blood thinning medications.
Menthol or capsaicin creams block the transmission of pain signals from your joints.
Immunosuppressants like prednisone or cortisone help reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment:
Surgery procedures accompanies
- Synovectomy
- Tendon repair.
- Joint fusion.
- Total joint replacement.

[…] Arthritis, a common degenerative disorder […]
Arthritis is an common issue now a day. After reading this article, you get aware of their early sigh and take initial step to manage this disorder.
This disorder is common now a days and everyone needs to know about it. Thanks for this great piece.
Informative 👍👍